经典排序算法之选择排序
选择排序是一种简单直观的排序算法,它的核心思想是“每次找到最小值并交换”。
基本思想
- 从待排序数组中找到最小(或最大)元素。
- 将该元素与数组的第一个位置元素交换。
- 对剩余的元素重复上述过程,直到整个数组排序完成。
换句话说,每次循环会把未排序部分的最小值放到当前排序位置。
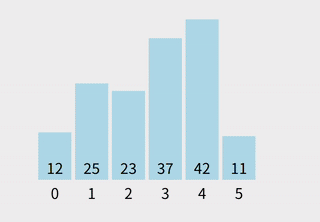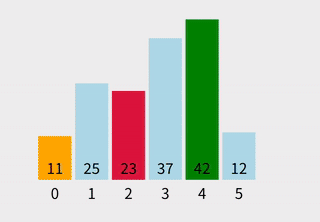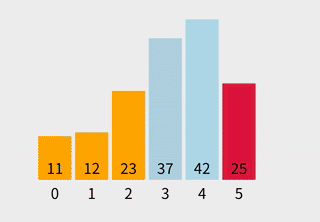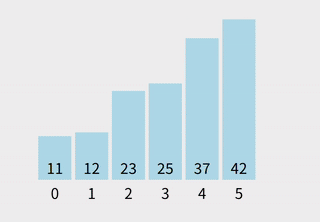
步骤举例
假设数组为 [29, 10, 14, 37, 13]:
- 第一次循环:找到最小值
10,与第一个元素29交换 →[10, 29, 14, 37, 13] - 第二次循环:在
[29, 14, 37, 13]中找到最小值13,与第二个元素29交换 →[10, 13, 14, 37, 29] - 第三次循环:在
[14, 37, 29]中最小值是14,位置正确,无需交换 →[10, 13, 14, 37, 29] - 第四次循环:在
[37, 29]中最小值是29,与37交换 →[10, 13, 14, 29, 37] - 完成排序。
Go 语言实现
go
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
// SelectionSort 实现选择排序
func SelectionSort(arr []int) {
n := len(arr)
for i := 0; i < n-1; i++ {
minIndex := i
// 找到剩余部分的最小值索引
for j := i + 1; j < n; j++ {
if arr[j] < arr[minIndex] {
minIndex = j
}
}
// 交换当前元素和最小值
if minIndex != i {
arr[i], arr[minIndex] = arr[minIndex], arr[i]
}
}
}
func main() {
arr := []int{29, 10, 14, 37, 13}
fmt.Println("排序前:", arr)
SelectionSort(arr)
fmt.Println("排序后:", arr)
}输出结果:
排序前: [29 10 14 37 13]
排序后: [10 13 14 29 37]选择排序特点
- 时间复杂度:O(n²)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)(原地排序)
- 稳定性:不稳定(因为交换可能改变相等元素的顺序)
参考
- https://leetcode.cn/discuss/post/3143970/xiang-jie-qi-da-chang-jian-pai-xu-suan-f-gqno/
- https://javaguide.cn/cs-basics/algorithms/10-classical-sorting-algorithms.html
- https://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/ten-sorting-algorithm.html
- https://github.com/MisterBooo/Article
- https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ur4y1w7tv/